Progressive die stamping is a sophisticated and highly efficient manufacturing process used extensively in the metalworking industry. It involves a series of automated steps that transform raw metal sheets into complex parts through sequential operations. This method is integral to producing components for a wide array of industries, including automotive, electronics, and appliances.
Understanding Progressive Die Stamping
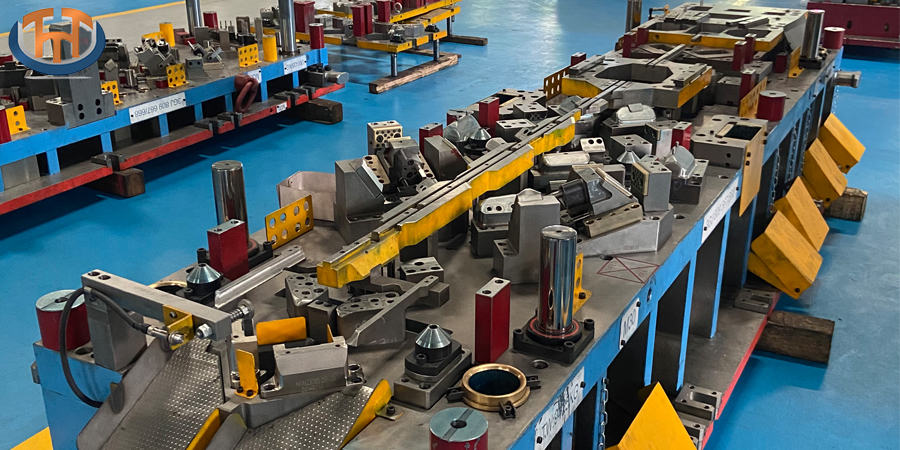
At its core, progressive die stamping uses a series of stations within a single die. Each station performs a distinct operation on the metal strip as it advances through the press. These operations can include cutting, bending, punching, and coining. The process begins with a metal strip being fed into the press. As the press cycles, the strip is advanced precisely to the next station, where another specific task is performed. This progression continues until the final product is completed and separated from the remaining strip.
Key Components and Process Flow
Strip Feeder: This is the starting point where the metal strip is fed into the die. It ensures consistent and precise feeding, which is crucial for maintaining the quality and accuracy of the stamped parts.
Die Stations: Each die station within the progressive die has a specific function. The metal strip moves from one station to the next, where operations such as piercing (creating holes), blanking (cutting out a shape), bending (forming the metal), and coining (stamping fine details) are performed in a precise sequence.
Press Machine: The press machine provides the necessary force to carry out the stamping operations. It can be mechanical or hydraulic, depending on the requirements of the job. Mechanical presses are known for their high-speed operation, while hydraulic presses offer superior control and flexibility.
Pilot Pins: These are critical components that ensure the strip is accurately positioned as it moves through each station. Pilot pins enter pre-punched holes in the strip, aligning it precisely for each operation.
Advantages of Progressive Die Stamping
Efficiency and Speed: One of the primary advantages of progressive die stamping is its ability to produce large quantities of parts rapidly. The continuous movement of the strip through the die stations allows for high-speed production, significantly reducing manufacturing time.
Cost-Effectiveness: Progressive die stamping minimizes material waste and labor costs. The automation of the process means fewer manual interventions are needed, reducing the likelihood of errors and increasing overall efficiency.
Consistency and Precision: This method ensures high levels of precision and repeatability. Each part produced is nearly identical to the others, which is crucial for industries that require uniform components, such as automotive and electronics manufacturing.
Versatility: Progressive die stamping can handle a variety of materials, including aluminium, steel, copper, and brass. It is also capable of producing complex geometries that would be challenging to achieve through other manufacturing processes.
Applications
The applications of progressive die stamping are vast and varied. In the automotive industry, it is used to create parts such as brackets, clips, and connectors. In electronics, it helps produce intricate components like terminals and contacts. The appliance industry relies on progressive die stamping for parts such as hinges and fasteners. Its ability to produce detailed and precise parts makes it indispensable in manufacturing sectors requiring high-volume, high-precision components.
Conclusion
Progressive die stamping stands out as a pivotal technology in modern manufacturing, combining efficiency, precision, and versatility. Its ability to produce high volumes of complex parts with consistent quality makes it a preferred method for many industries. As technology advances, progressive die stamping continues to evolve, promising even greater innovations and improvements in manufacturing capabilities.
Post time: May-24-2024


.png)
.png)