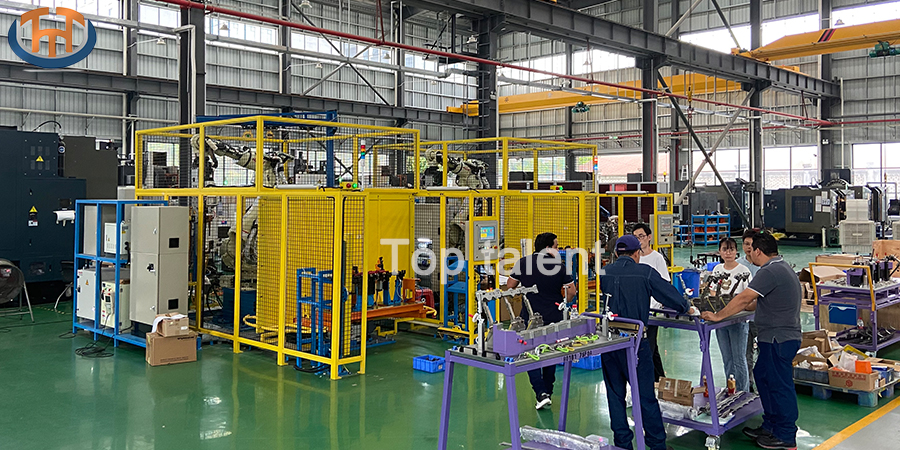
Welding Cells is A Critical Tool for Modern Manufacturing
Welding cells play a crucial role in modern manufacturing processes, particularly in industries that require precision and efficiency. These are specialized setups designed to streamline and automate the welding process. By combining robotic systems with advanced welding technology, welding cells ensure consistent quality and high production rates, making them invaluable in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery.
Components of a Welding Cell
A typical welding cell consists of several key components: robotic arms, welding tools, power sources, and safety enclosures. The robotic arm holds the welding tool and moves it with high precision to ensure accurate welds. The power source provides the energy needed for the welding process, which could involve various methods such as MIG (Metal Inert Gas), TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), or spot welding. Safety measures are a crucial part of the setup, as the welding process involves high heat and intense light. These cells are enclosed in protective barriers, with sensors and emergency stop mechanisms in place to prevent accidents.
Types of Welding Cells
There are various types of welding cells, including fixed, flexible, and mobile configurations. Fixed welding cells are designed for repetitive, high-volume tasks, making them ideal for large-scale production environments. Flexible cells, on the other hand, can handle a variety of welding tasks, offering adaptability to changing production needs. Mobile welding cells can be transported across a facility, allowing for more versatility in handling different projects.
Benefits of Welding Cells
The benefits of using welding cells are numerous. First and foremost, they offer a high level of precision that is difficult to achieve with manual welding. The robotic systems are programmed to follow exact paths, ensuring consistent results across large production runs. This reduces the likelihood of human error and improves the overall quality of the welds.
Another significant advantage is efficiency. Welding cells can operate continuously with minimal downtime, unlike human welders who need breaks. This increased productivity translates to faster production cycles, helping manufacturers meet tight deadlines. Additionally, by automating the welding process, companies can reduce labour costs while maintaining a high standard of quality.
Applications Across Industries
Welding cells are widely used in various industries. In the automotive sector, they are essential for assembling vehicle components with precision and speed. The aerospace industry relies on welding cells to produce aircraft parts that meet stringent safety and durability standards. Even in heavy machinery manufacturing, welding cells ensure that large metal structures are securely and accurately assembled.
Future Trends
As technology evolves, welding cells are becoming more advanced. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being integrated to optimize the welding process further, enabling cells to adapt to complex welding challenges. In the future, we can expect welding cells to become even more efficient, versatile, and intelligent, further transforming manufacturing practices.
Post time: Oct-17-2024


.png)
.png)