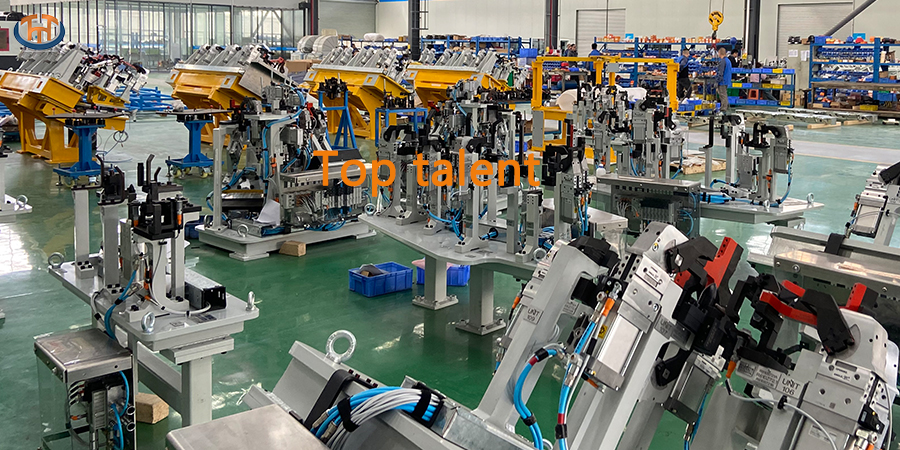
 In manufacturing and metal fabrication, welding is a cornerstone of the structural integrity and durability of countless products. However, not all welding processes are created equal, and the tools used to facilitate these processes-such as arc welding equipmentand spot welding fixtures-are designed for specific purposes. While both are essential in their respective applications, they differ significantly in design, functionality, and use cases. Understanding these differences is critical to optimizing production efficiency and ensuring quality welds.
In manufacturing and metal fabrication, welding is a cornerstone of the structural integrity and durability of countless products. However, not all welding processes are created equal, and the tools used to facilitate these processes-such as arc welding equipmentand spot welding fixtures-are designed for specific purposes. While both are essential in their respective applications, they differ significantly in design, functionality, and use cases. Understanding these differences is critical to optimizing production efficiency and ensuring quality welds.
Arc Welding Jigs: Precision and Flexibility
Arc welding jigs are specialized tools used to hold and position workpieces during arc welding processes, such as shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), gas metal arc welding (GMAW), or tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding. These jigs are designed to ensure that the components being welded remain in the correct alignment and orientation throughout the process. This is particularly important for complex or multi-part assemblies where even minor misalignments can lead to defects or structural weaknesses.
One of the defining features of arc welding jigs is their adaptability. They are often custom-built to accommodate specific workpiece geometries, making them highly versatile for unique or low-volume production runs. For example, a jig might include adjustable clamps, brackets, or supports to secure irregularly shaped parts. Additionally, arc welding jigs are typically designed to withstand the high heat and spatter generated during arc welding, often incorporating heat-resistant materials or protective coatings.
Arc welding jigs also play a critical role in ensuring repeatability. By holding parts in a consistent position, they enable welders to produce uniform results across multiple units. This is especially important in industries like aerospace or automotive manufacturing, where precision is paramount.
Spot Welding Fixtures: Speed and Consistency
In contrast, spot welding fixtures are tailored for resistance spot welding, a process that joins metal surfaces by applying heat and pressure at specific points. Unlike arc welding, which creates a continuous weld along a seam, spot welding produces a series of discrete weld “spots” to bond materials together. This method is commonly used in the automotive industry for assembling sheet metal components, such as car bodies.
Spot welding fixtures are designed to maximize efficiency and consistency. They typically consist of electrodes that deliver the electrical current needed to generate the weld and mechanisms to apply the necessary pressure. The fixtures are often automated or semi-automated, allowing for rapid production cycles. For instance, in a high-volume automotive assembly line, spot welding fixtures can complete hundreds of welds per hour with minimal human intervention.
One key difference between spot welding fixtures and arc welding jigs is their focus on localized precision. While arc welding jigs must accommodate the entire workpiece, spot welding fixtures are concerned only with the specific areas where the weld spots will be applied. This localized approach allows for greater speed and reduces the complexity of the fixture design. However, it also means that spot welding fixtures are less versatile and are often dedicated to a single type of workpiece or assembly.
Key Differences at a Glance
Purpose: Arc welding jigs are used for continuous welding processes, while spot welding fixtures are designed for localized, point-based welding.
Design Complexity: Arc welding jigs are often more complex and customizable to accommodate various workpiece shapes, whereas spot welding fixtures are simpler and more specialized.
Heat Management: Arc welding jigs must withstand prolonged exposure to high heat, while spot welding fixtures are designed for short, intense bursts of heat.
Production Speed: Spot welding fixtures are optimized for high-speed, high-volume production, whereas arc welding jigs are better suited for precision and flexibility in lower-volume or custom applications.
Conclusion
Both arc welding jigs and spot welding fixtures are indispensable tools in modern manufacturing, but they serve distinct purposes. Arc welding jigs excel in providing precision and adaptability for complex or custom welding tasks, while spot welding fixtures prioritize speed and consistency for high-volume production. By understanding each tool’s unique strengths and limitations, manufacturers can choose the right tool for the job, ensuring optimal results and efficient workflows. Whether you’re crafting a one-of-a-kind prototype or mass-producing automotive components, the right welding tool can make all the difference.
Post time: Feb-21-2025

.png)
.png)