The Evolution and Benefits of Automatic Welding Lines
In modern manufacturing, efficiency and precision are critical, especially in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. One of the most significant advancements in these sectors has been the development of automatic welding lines. These systems have revolutionized the welding process, offering increased productivity, enhanced quality control, and reduced human error. This article explores the workings of automatic welding lines and their advantages in today’s industrial landscape.
What is an Automatic Welding Line?
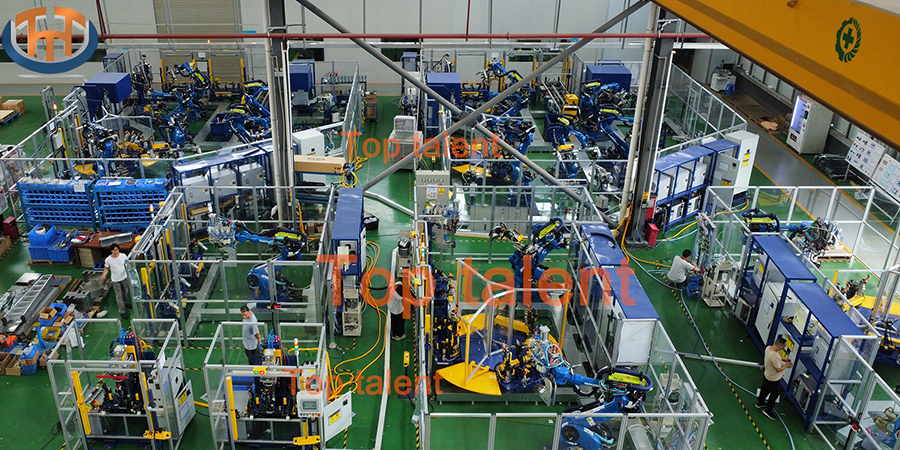
An automatic welding line refers to a fully automated system that performs welding tasks without direct human intervention. These lines integrate robotic arms, conveyor systems, sensors, and advanced welding equipment to complete welding processes continuously and with high precision. Typically used in large-scale production environments, these systems are designed to perform repetitive and complex welding operations with remarkable accuracy.
Automated welding lines often feature various types of welding techniques, including MIG (Metal Inert Gas), TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), and laser welding. The choice of welding method depends on the specific application and materials used, whether it’s steel, aluminium, or other alloys. The automated systems are programmed to follow predefined welding paths and procedures, ensuring uniform weld quality across all workpieces.
Key Components of Automatic Welding Lines
Automatic welding lines are complex systems that consist of several components working together in sync. Here are some of the critical elements:
Robotic Arms: These are the most visible part of the system. The robotic arms manipulate the welding tool, ensuring that the weld is applied at the correct angle and location. These arms can be programmed to move in multiple directions, making them highly versatile for different welding tasks.
Conveyor Systems: Conveyors transport materials or parts through the welding line. This movement allows for continuous operation and streamlines the manufacturing process, minimizing downtime between welding stages.
Sensors and Cameras: Sensors detect the position and orientation of the parts to be welded, ensuring precise alignment. Cameras may be integrated for real-time monitoring, providing feedback to the system for any necessary adjustments.
Welding Machines: Depending on the type of welding required, these machines generate the heat needed to fuse the materials together. Laser welding machines, for example, use focused light to create high-quality welds with minimal distortion, while traditional arc welders are suited for thicker metals.
Advantages of Automatic Welding Lines
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: One of the most apparent advantages of automated welding lines is the ability to increase production speed. Since the system operates continuously, it can weld more parts in a given timeframe compared to manual processes. Additionally, these systems can run 24/7 with minimal supervision, maximizing output in high-demand industries.
Consistent Quality: In welding, consistency is key to ensuring the strength and durability of the final product. Human welders, despite their expertise, may introduce slight variations in their welds. Automated systems, however, perform with a high degree of accuracy and repeatability, ensuring uniformity across all parts.
Reduced Labor Costs and Risk: By minimizing human involvement in the welding process, companies can reduce labour costs and improve worker safety. Welding can be hazardous, involving exposure to extreme heat, ultraviolet light, and fumes. Automation reduces the need for human welders to be in close proximity to these dangers, significantly lowering the risk of accidents.
Greater Flexibility and Scalability: Modern automatic welding lines can be easily reprogrammed to accommodate different tasks, making them highly adaptable to various production needs. As demand increases, the system can be scaled up without requiring significant retooling, further enhancing productivity.
Data Collection and Monitoring: Automation allows for detailed data collection, helping manufacturers analyze the welding process in real time. Information such as temperature, speed, and weld quality can be monitored, enabling quick adjustments to optimize the process.
Conclusion
Automatic welding lines are a game-changer for industries that require high-volume, precise, and consistent welding. Their ability to enhance productivity, reduce labour costs, and maintain consistent quality makes them an essential tool in modern manufacturing. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated welding systems that push the boundaries of efficiency and automation.
Post time: Sep-13-2024


.png)
.png)