Creating a welding fixture is a complex and highly specialized process that involves various stages of design, fabrication, and testing. These fixtures play a critical role in ensuring the precision and quality of welded joints in a wide range of industries, from automotive manufacturing to aerospace.
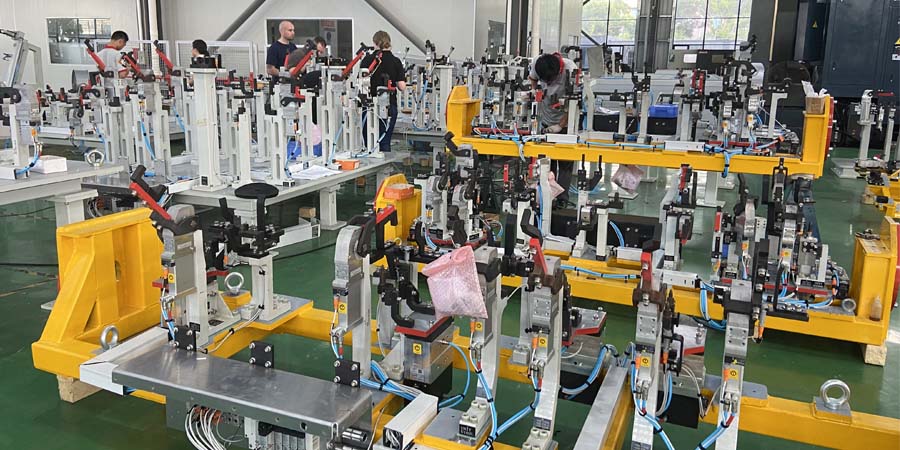

1. Design and Engineering:
Welding fixture manufacturing begins with the design and engineering phase. Here, a team of skilled engineers and designers works closely with the client to understand their specific welding requirements and project goals. The design process includes the following key steps:
Conceptualization: The initial step involves conceptualizing the fixture’s purpose, size, and configuration. Engineers consider factors such as the type of welding (e.g., MIG, TIG, or resistance welding), material specifications, and the workpiece’s dimensions.
CAD (Computer-Aided Design): Using advanced CAD software, engineers create detailed 3D models of the fixture. These models allow for a precise visualization of the fixture’s components, including clamps, supports, and positioning elements.
Simulation: Simulations are conducted to ensure that the fixture design will meet the project’s welding needs. Engineers use finite element analysis (FEA) to assess the fixture’s structural integrity and stress distribution.
Material Selection: The choice of materials for the fixture is vital. Engineers select materials that can withstand the heat, pressure, and potential wear and tear associated with welding. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and specialized alloys.
Clamping and Positioning Strategy: Engineers develop a clamping and positioning strategy to securely hold the workpiece during welding. This strategy may involve adjustable clamps, hydraulics, or other mechanisms tailored to the specific project.
2. Prototype Development:
Once the design is finalized, the next step is to create a prototype. This is a crucial phase in the welding fixture manufacturing process, as it allows for testing and refinement of the fixture design. The prototype development process typically includes the following steps:
Fabrication: Skilled welders and machinists fabricate the prototype fixture according to the CAD design. Precision is essential to ensure that the fixture’s components fit together accurately.
Assembly: The various components of the fixture, including clamps, supports, and positioners, are assembled according to the design specifications.
Testing: The prototype is rigorously tested in a controlled environment to ensure that it meets the project’s requirements. This may involve conducting sample welds to assess the fixture’s performance, accuracy, and repeatability.
Adjustments and Refinements: Based on the testing results, adjustments and refinements are made to the fixture design as needed to optimize its functionality.
3. Production and Fabrication:
Once the prototype has been successfully tested and refined, it’s time to move into full-scale production. The fabrication of welding fixtures at this stage involves several key processes:
Materials Procurement: High-quality materials are sourced in the required quantities. This may include various types of steel, aluminium, fasteners, and specialized components.
CNC Machining: Computer numerical control (CNC) machines are used to create precise components for the fixtures. This includes cutting, drilling, milling, and other machining processes to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Welding and Assembly: Skilled welders and technicians assemble the fixture components, ensuring that they meet the exact specifications of the design. This may involve welding, bolting, and precision assembly techniques.
Quality Control: Throughout the production process, quality control measures are in place to inspect and verify the accuracy, durability, and functionality of the fixtures.
4. Installation and Integration:
Once the welding fixtures are fabricated, they are installed and integrated into the client’s manufacturing environment. This phase includes the following steps:
Installation at Client Site: A team of experts from the welding fixture manufacturer installs the fixtures at the client’s facility. This may involve bolting the fixture to the floor, ceiling, or other suitable support structures.
Integration with Welding Equipment: The fixtures are integrated with the client’s welding equipment, whether it’s manual welding stations, robotic welding cells, or other machinery. This integration ensures seamless operation and synchronization with the welding process.
Training and Documentation: The manufacturer provides training to the client’s personnel on how to use and maintain the fixtures. Comprehensive documentation and user manuals are also supplied.
5. Ongoing Support and Maintenance:
Welding fixture manufacturers often offer ongoing support and maintenance services to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of the fixtures. These services may.
Post time: Nov-03-2023

.png)
.png)